Tambien hay una version en castellano de este post, click aca.
Welcome to the post, today we’ll talk about the different operators.
Arithmetic operators
| Operator | Description |
| + | Addition |
| – | Subtraction |
| * | Multiplication |
| / | Division |
| \ | Integar division |
| ~ | Negation |
| ^ | Exponentiation |
| = | Assign |
These operators make basical mathematical operations and we can used it combined between they.
Concatenation operator
| Operator | Description |
| & | Concatenate |
This operator allows us to join two texts.
Relational operators
| Operator | Description |
| = | Equal |
| <> | Different |
| < | Lesser than |
| > | Greater than |
| <= | Lesser or equal than |
| >= | Greater or equal than |
These operators compare two values and return a boolean value. When satisfied, it returns true; otherwise it is false. For example, you can have these values:
30 <> 40
25 < 30
25 > 30The first example returns a true value because they’re differents. The second example returns true too. Because of the first value is lesser than the second and the third example returns a false value because it isn’t satisfied the comparation.
Logical Operators
| Operator | Description |
| not | Turn the value to inverse |
| and | check if both values are the same |
| or | check if one value is true |
| xor | returns false if both values are the same |
| eqv | it’s similar to equal operator |
| imp | check implication between values |
These operators evaluate between two boolean values and returns another boolean value. Let’s take a look for the following examples:These operators evaluate between two boolean values and returns another boolean value. Let’s take a look for the following examples:
true and true
true or false
not trueThe first case returns a boolean value of true because both values are true. The following case returns a true value because only one is true and the final example returns a false value. Because always returns contrary value.
Others
| Operator | Description |
| is | Comparation between objects |
This operator is used to check if an object is from some type of data. For example, we’ve the function isnumber to check if the object is a number. Let’s a look to an example, create a new file with the following code:
const value_1 = 10
const value_2 = 30
const value_3 = true
const value_4 = false
msgbox value_1 < value_2,,"Operators sample"
msgbox value_1 > value_2,,"Operators sample"
msgbox value_3 or value_4,,"Operators sample"
msgbox not value_3,,"Operators final"First, we define four constants. The first two are with number values and the other two are boolean values. Then, with msgbox we’ll show the value returned by the operator. Let’s watch the first msgbox output:
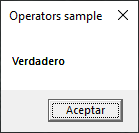
This is true because value_1 is lesser than value_2. Let’s watch now the second msgbox:
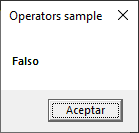
Now, it’s false because value_1 is not greater than value_2. Let’s watch the third msgbox:

Again, this is true because only one of both values is true and this operator returns true with this condition. Let’s watch the final msgbox:
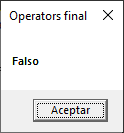
This returns false because this operator always inverts the received value. These operators are used in conditionals, loops or another functions where we must evaluate a condition.
Note:
Excuse by the pictures but my laptop is in spanish.
In summary, we saw to the available operators in the language, what they’re, how to use it, the returned values, an example and where can be used it. I hope you’ve found it useful. You can follow me on this social networks:


Donatión
It’s for site maintenance, thanks!
$1.50

